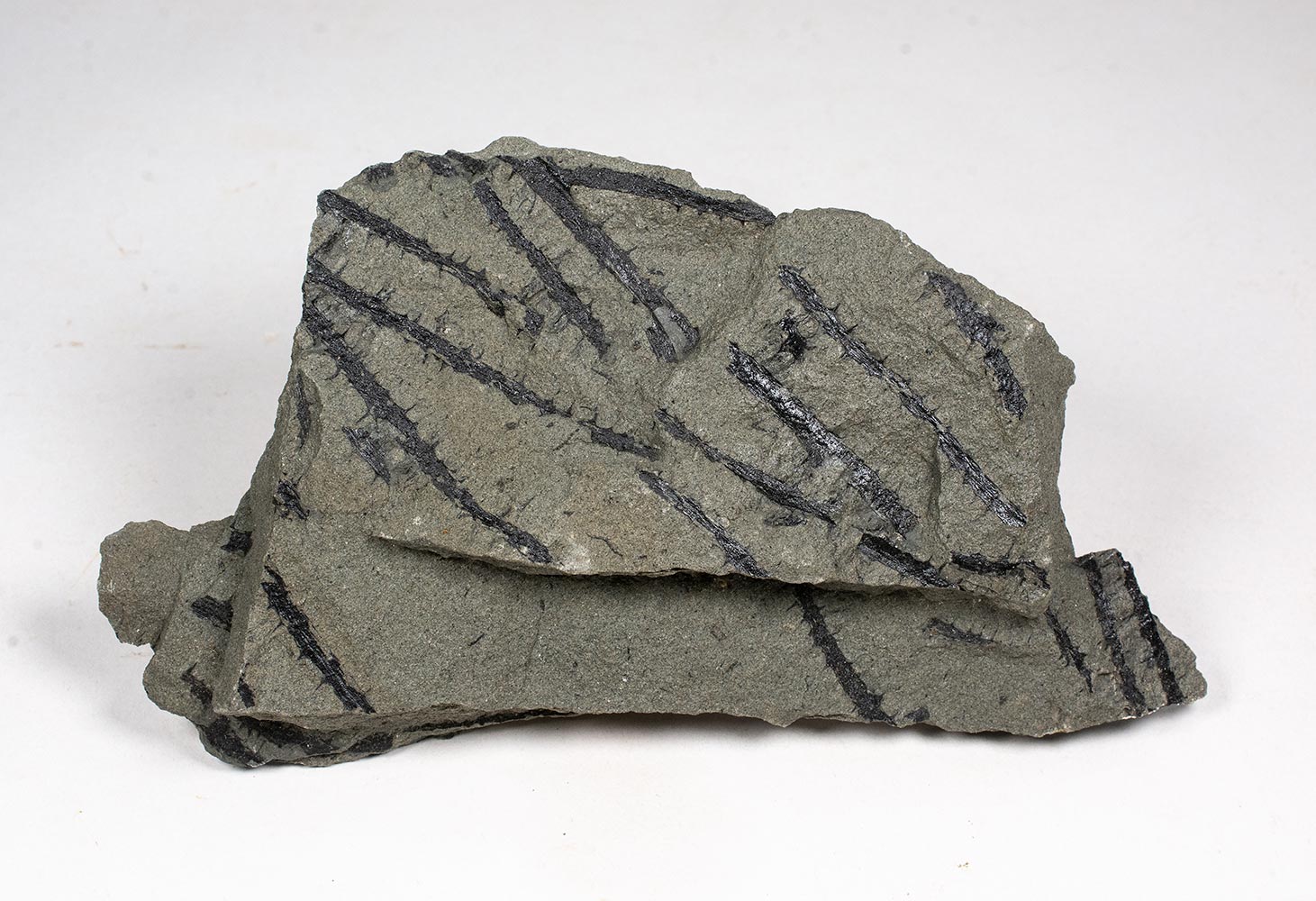
Description
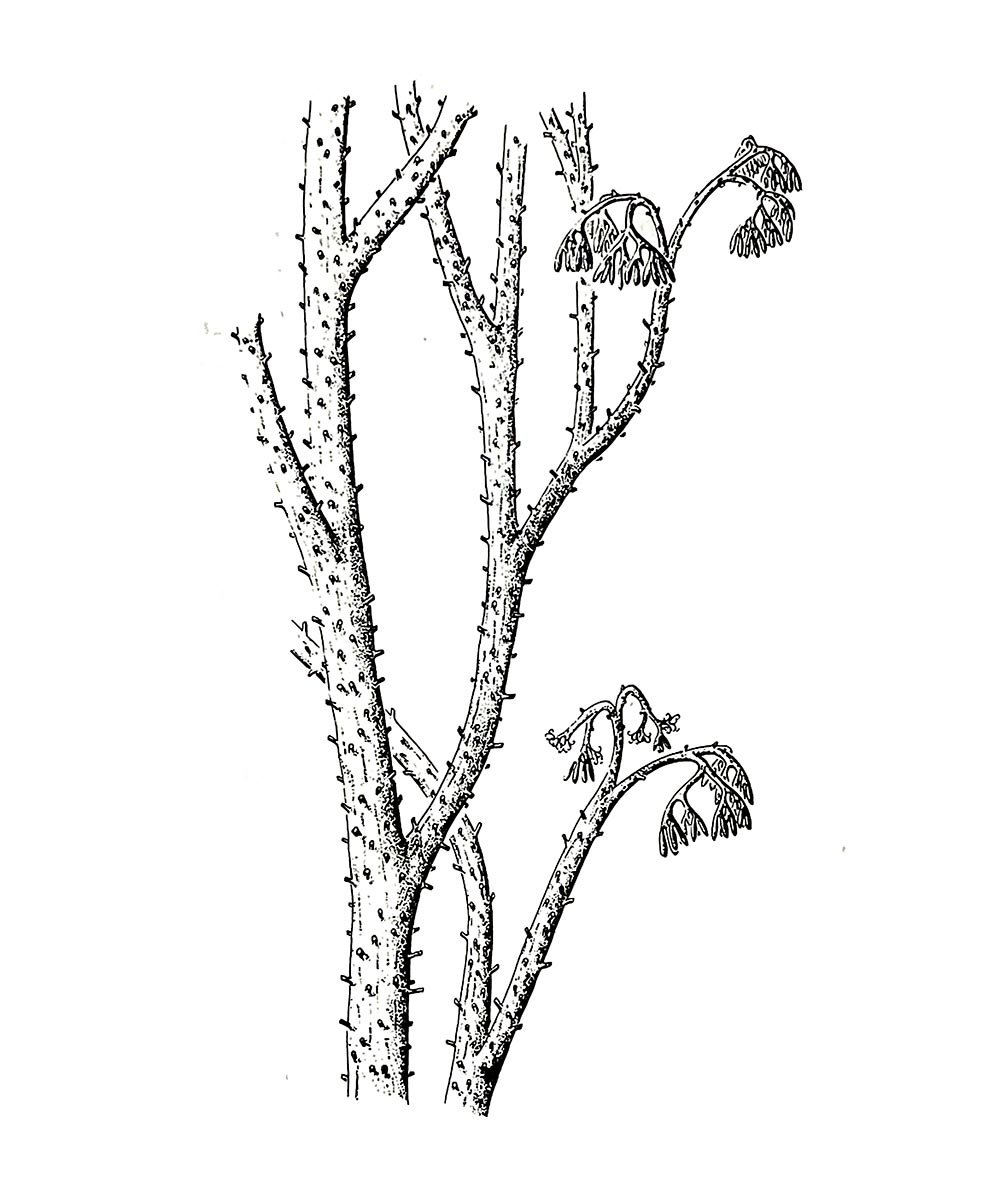
Psilophyton princeps
Early Devonian
Gaspe Sandstone
Gaspe, Newfoundland, Canada
155mm slab covered with Psilophyton stems.
Psilophyton is an extinct genus of primitive vascular plants that lived during the Devonian period, around 420 to 360 million years ago. It is one of the earliest known genera of land plants, providing important insights into the evolution of terrestrial flora. Fossils of Psilophyton have been found in regions of present-day North America and Europe. First described in 1859, it was one of the first fossil plants recognized as Devonian and has been a core of research now for almost two centuries.
Psilophyton had simple branching stems, lacked true leaves and roots, and reproduced using spores, much like ferns and other spore-bearing plants. It was likely among the first plants to establish itself on land, contributing to the formation of early terrestrial ecosystems. The study of Psilophyton has helped scientists understand the transition from aquatic to terrestrial environments in plant evolution, a key step that paved the way for more complex plants and, eventually, the forests we see today.